
There are many reasons why someone might choose to use a VPN. One of the most common reasons is to protect their privacy. With a VPN, your internet activity is hidden from your ISP and other third-parties, preventing them from collecting your browsing data, such as your search history and online behavior. This is particularly important for those who want to keep their online activities private, such as journalists, activists, and whistleblowers.
VPNs can also enhance security by encrypting your internet connection, making it difficult for hackers to intercept your online communications. This is particularly crucial when using public Wi-Fi, which is often insecure and can leave you vulnerable to cyber-attacks.
In addition, VPNs can help you access geo-restricted content by changing your IP address to that of a country where the content is available. For example, if you're traveling outside of the United States but still want to access US-based streaming services such as Netflix or Hulu, you can connect to a VPN server located in the US to unblock the content.
However, it's worth noting that not all VPNs are created equal. Some VPN providers keep logs of your online activities, which could compromise your privacy. It's important to choose a VPN provider that has a strict no-logs policy, which means they don't collect any information about your online activities.
Furthermore, some VPNs may slow down your internet connection due to the encryption process. While this is not necessarily a deal-breaker, it's worth considering if you have a slow internet connection to begin with.
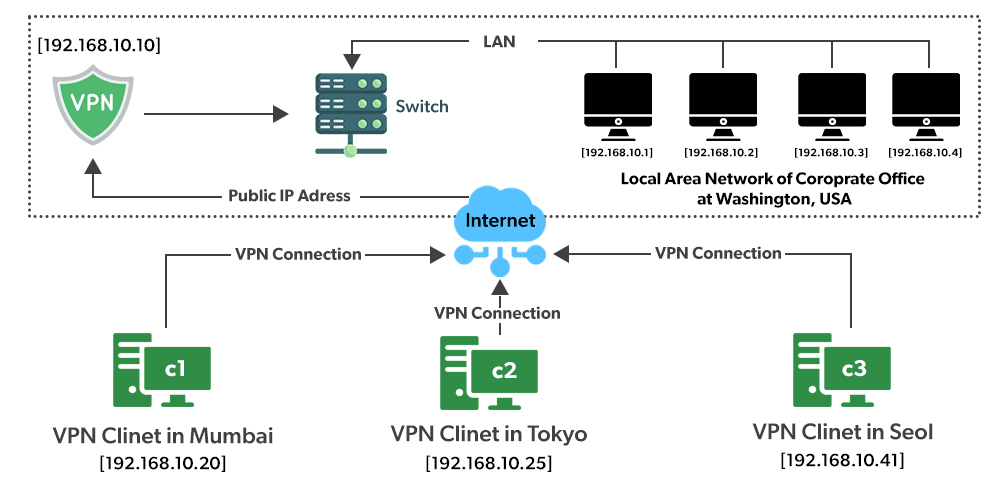
The architecture of a VPN can vary depending on the type of VPN and its intended use case. However, there are some common components that are present in most VPN architectures.
The first component is the VPN client: This is the software installed on the user's device, such as a laptop, smartphone, or tablet. The VPN client is responsible for initiating the connection to the VPN server and managing the encrypted tunnel between the client and the server.
The second component is the VPN server: This is the endpoint that receives the encrypted traffic from the VPN client and decrypts it before forwarding it to its final destination on the internet. The VPN server can be located in a data center, on-premises, or in the cloud.
The third component is the VPN protocol: This is the set of rules that define how the VPN client and server communicate with each other and how the encrypted tunnel is established. There are several VPN protocols available, including OpenVPN, PPTP, L2TP/IPsec, and IKEv2.
The fourth component is the encryption algorithm: This is the mathematical formula used to scramble the data before it is transmitted over the internet. The most commonly used encryption algorithms in VPNs are AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman).
The fifth component is the authentication mechanism: This is the process used to verify the identity of the user and the VPN server. The most common authentication mechanisms in VPNs are username/password, digital certificates, and two-factor authentication.
In addition to these components, some VPN architectures may include additional features such as load balancing, failover, and split tunneling. Load balancing is used to distribute VPN traffic across multiple VPN servers to ensure optimal performance and availability. Failover is used to automatically switch to a backup VPN server in case the primary server goes down. Split tunneling is used to allow some traffic to bypass the VPN tunnel and be sent directly over the internet, while other traffic is encrypted and sent through the VPN tunnel.
Overall, the architecture of a VPN is designed to provide a secure and encrypted connection between the user's device and the internet. By using a VPN, users can protect their online privacy and security, access geo-restricted content, and bypass censorship.
In conclusion, VPNs are a valuable tool for enhancing online privacy,
security, and accessing geo-restricted content. However, it's crucial to
choose a reputable VPN provider that prioritizes user privacy and
doesn't log your online activities. With the right VPN, you can enjoy
the internet with peace of mind, knowing that your online activities are
private and secure.

