In today's world of rapidly growing data, businesses need advanced tools
to manage and analyze vast amounts of data. Online Analytical
Processing (OLAP) servers are one such tool that enables businesses to
gain insights from their data in real-time.
OLAP servers are databases optimized for analyzing and reporting on large amounts of data. They provide the ability to perform complex queries quickly and efficiently, making them ideal for decision-making, forecasting, and trend analysis.
The architecture of an OLAP server consists of three main components: the data source, the OLAP engine, and the client application.
Data Source:
The data source is where the
OLAP server retrieves its data. This can be a relational database, a
flat file, or any other data repository that can be accessed by the OLAP
server. The data source must be well-designed and optimized for OLAP
processing, as this will greatly impact the performance of the OLAP
server.
OLAP Engine:
The OLAP engine is the heart of the
OLAP server. It is responsible for processing and analyzing the data
retrieved from the data source. The OLAP engine performs a number of
operations, including data aggregation, slicing, and dicing. The OLAP
engine also stores metadata about the data, such as dimensions,
measures, and hierarchies, which are used to organize and analyze the
data.
The OLAP engine can be divided into two main components:
the Storage Engine and the Calculation Engine. The Storage Engine is
responsible for storing and retrieving the data, while the Calculation
Engine is responsible for performing the calculations and aggregations
required for data analysis.
Client Application:
The client application is the user interface through which users interact with the OLAP server. The client application allows users to browse the data, create reports, and perform ad-hoc analysis. The client application can be a web-based application, a desktop application, or a mobile application.
The client application communicates with the
OLAP engine through a middleware layer, which handles the communication
between the client application and the OLAP engine. The middleware layer
can be a simple HTTP server or a more complex middleware platform that
provides additional features such as security and authentication.
OLAP
servers come in different types, each designed to meet specific
business needs. Let's explore the different types of OLAP servers:
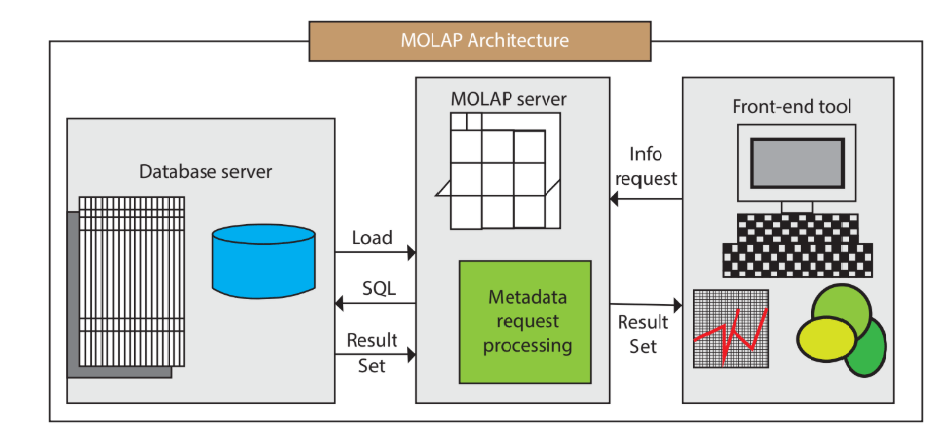
Multidimensional OLAP (MOLAP) Server: MOLAP servers are the most traditional OLAP servers, and they store data in a multidimensional cube format. The data is pre-aggregated and organized in dimensions such as time, geography, and product. MOLAP servers offer excellent query performance and can handle large amounts of data.
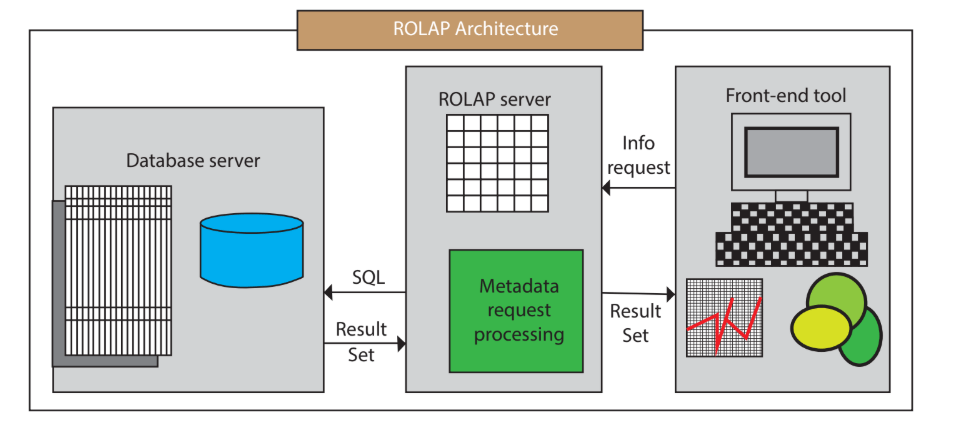
- Relational OLAP (ROLAP) Server: ROLAP servers store data in a relational database format, similar to traditional databases. ROLAP servers use SQL to create dynamic queries that access the data stored in the database. ROLAP servers are scalable and can handle large amounts of data, but they can be slower than MOLAP servers.
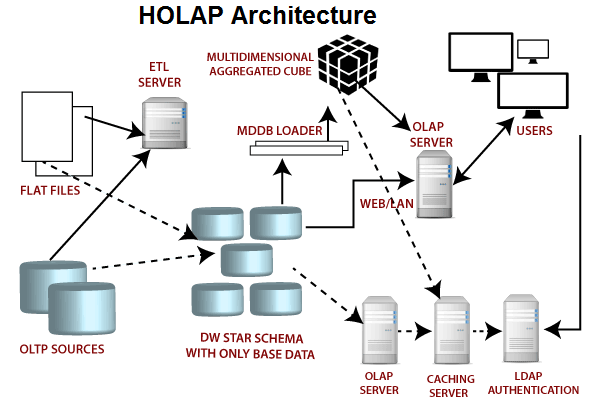
- Hybrid OLAP (HOLAP) Server: HOLAP servers combine the best features of MOLAP and ROLAP servers. They store summary data in a multidimensional format and detail data in
a relational database format. HOLAP servers offer excellent query
performance and scalability, making them ideal for large enterprises.
- In-Memory OLAP (IOLAP) Server: IOLAP
servers store data in memory instead of on disk, resulting in faster
query performance. IOLAP servers use columnar storage to optimize
performance, and they can handle large amounts of data. However, IOLAP
servers can be expensive due to their memory requirements.
- Desktop OLAP (DOLAP) Server: DOLAP
servers are designed for small-scale analysis and run on individual
computers. They are used by individuals or small teams for quick
analysis of data. DOLAP servers are easy to use and do not require
extensive IT expertise.
In conclusion, OLAP servers are powerful tools for data analysis and reporting. Each type of OLAP server has its own advantages and disadvantages, and businesses should choose the type that best suits their needs. With the right OLAP server, businesses can gain valuable insights from their data and make informed decisions

